To locate specific information on a graph—such as a time, number, or specific text like a person's name—you can use the Filters or Quick Find features in Maltego Graph (Browser.)
Filters in Maltego Graph (Browser) allow investigators to search for properties within Entities, offering flexibility and precision to narrow down results. Filters support text, time, and number properties depending on the available data in the graph.
Types of Filters
- Text Filters
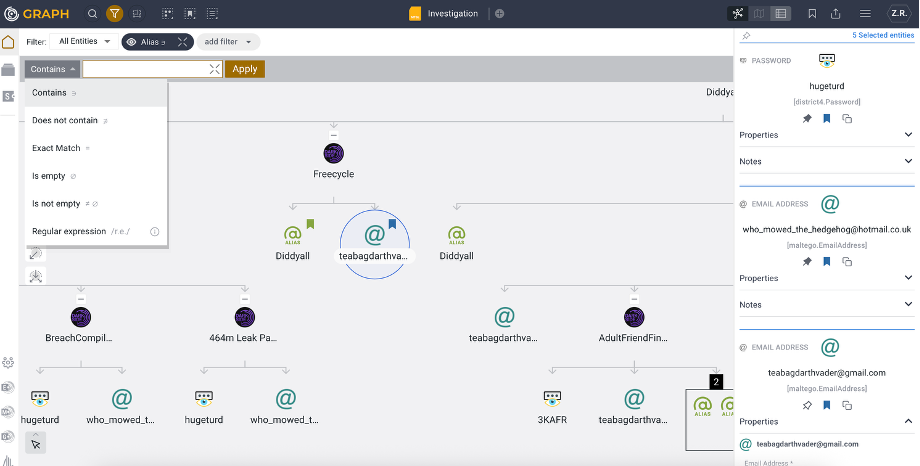
Text filters work with all properties, including time-based and numeric ones. After selecting a property, you can choose a logical operation. Common options include:- Contains: Matches Entities with the selected property containing the provided text.
- Does Not Contain: Matches Entities where the property value does not include the provided text.
- Exact Match: Matches Entities where the property value exactly matches the provided text, including case.
- Is Empty / Is Not Empty: Filters Entities based on whether a property is populated.
- Regular expression: Matches Entities where the property value conforms to a provided regular expression.
Tip: Use Large Language Models (LLMs) to simplify creating regex filters. Provide an example of your data structure and describe your filtering needs. The LLM can generate a regex pattern that you can easily copy and paste into Maltego Graph Browser's regex filter for advanced, flexible filtering. For example: "My dates are formatted as 1960/04/00. Give me a regex that filters all dates that are in April."- Time Filters
Time filters let investigators filter Entities over a time range, including optional time-of-day parameters.
- Number Filters
Number filters let investigator filter Entities if they contain number properties such as a count property.
Combining Filters
Filters can be combined without limits:
- AND (Default): Entities must match all active filters to be highlighted.
- OR: Entities matching any filter are highlighted.
Investigators can toggle filters on or off with the eye icon, making it easier to hide certain filters and refine results.
Why Use Filters?
Filters empower investigators to quickly narrow down data on a graph and find the most relevant Entities, streamlining their workflow in the following scenarios:
Identifying Key Targets in Complex Graphs
- Use Case: An investigator analyzing a graph with hundreds of Entities needs to identify individuals who are most frequently mentioned or connected.
- How Filters Help: Use Text Filters to search for specific names or terms, such as aliases, usernames, or email addresses.
Detecting Coordinated Campaigns
- Use Case: A social media investigator is tasked with finding accounts coordinating disinformation by analyzing user activity.
- How Filters Help: Use Text Filters to search for repeated hashtags, mentions, or links. Combine with Regex Filters to match specific patterns, such as bot-generated usernames.
Cleaning Up and Organizing the Graph
- Use Case: An investigator needs to declutter a graph by removing Entities with missing or incomplete information.
- How Filters Help: Use "Is Empty" Text Filters to highlight Entities with missing properties, such as blank names or unassigned IP addresses. These can then be easily removed or tagged for follow-up.
Quick Find
Quick Find in Maltego Graph (Browser) allows investigators to find Entities and their associated properties within the graph. This feature is particularly useful for pinpointing specific data points or connections in large and complex datasets.
How to Use Quick Find
To access the Quick Search feature:
- Click on the magnify icon next to the Graph logo in Maltego Graph (Browser).
- Enter your desired search term or phrase.
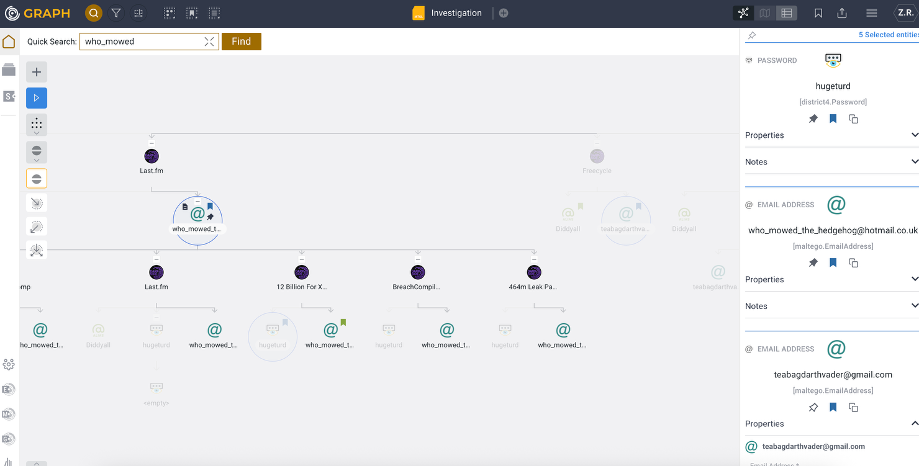
Example Use Case
In the example below, the email address who_mowed_the_hedgehog@hotmail.co.uk appears in two contexts:
- As a standalone Entity.
- As a property within the Compromised Record Entity.
Both instances are highlighted, enabling the investigator to quickly locate all occurrences of the email in the graph.